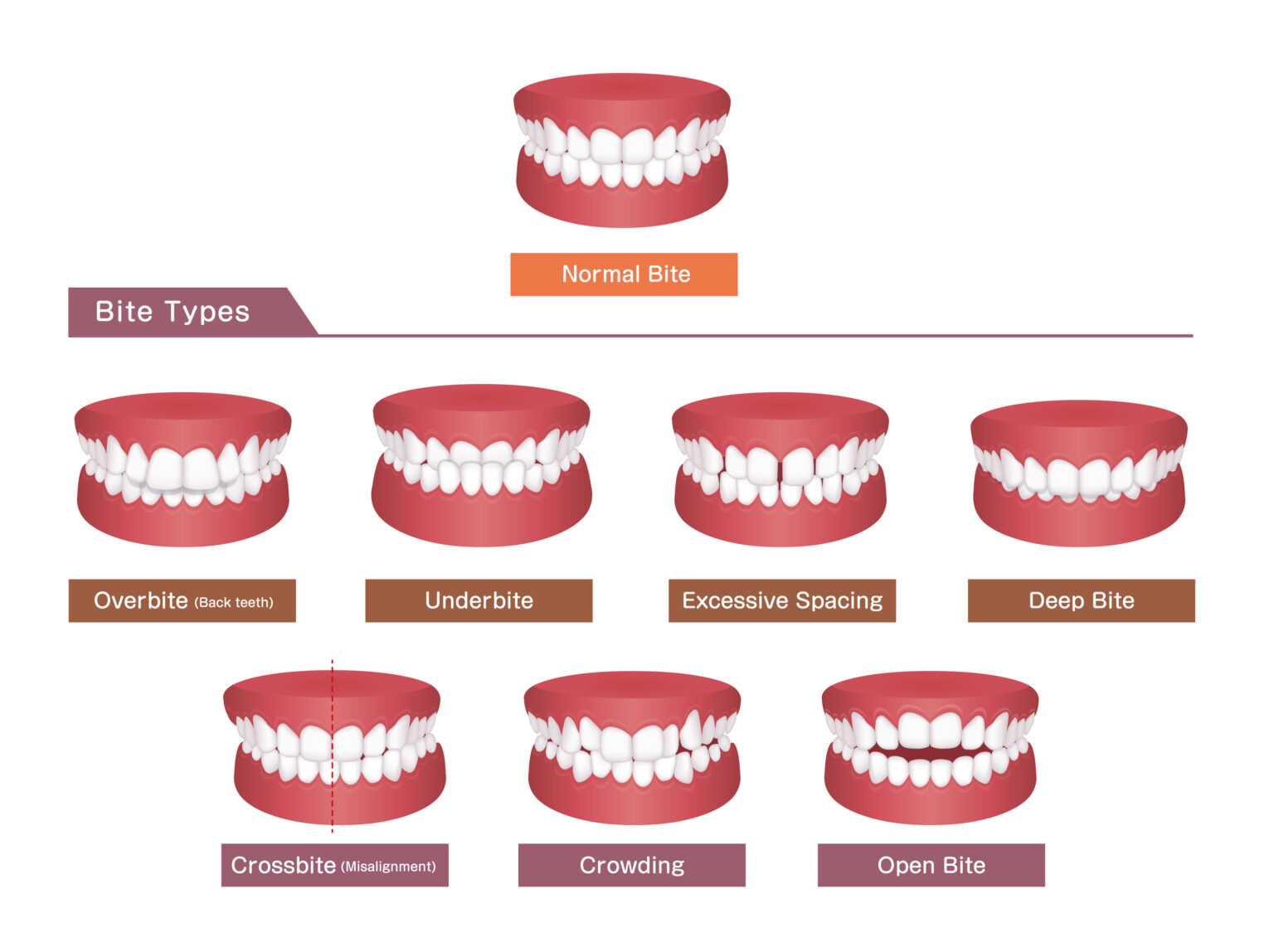
Having a normal bite is not only essential for a confident smile but also for overall dental health. Your bite refers to how your upper and lower teeth come together when you close your mouth. Ideally, your upper teeth should slightly overlap your lower teeth, creating a harmonious alignment. However, many individuals experience bite problems, such as overbites, underbites, excessive spacing, deep bites, crossbites, and crowding, which can affect both the aesthetics and functionality of their teeth.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the significance of having a normal bite, the different types of bite problems, their causes, and available treatment options. Whether you’re seeking to understand your own bite or the bite issues of a loved one, this article will provide you with valuable insights to make informed decisions about your dental health.
Table of Contents,
The Significance of a Normal Bite
A normal bite goes beyond cosmetic concerns. It plays a crucial role in maintaining proper oral function and preventing various dental problems. Here are some key reasons why a normal bite is important:
1. Effective Chewing and Digestion
A normal bite allows for efficient chewing, which is essential for breaking down food into smaller particles for proper digestion. When your teeth are misaligned, it can lead to difficulties in chewing, resulting in inadequate food breakdown and potential digestive issues.
2. Speech Clarity
Your bite also influences your ability to pronounce words clearly. Misaligned teeth can affect the position of your tongue and lips, causing speech impediments or difficulties in articulating certain sounds.
3. Balanced Jaw Function
A normal bite ensures that the forces exerted during biting and chewing are evenly distributed across your teeth and jaw joints. When your bite is off, it can lead to jaw pain, temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ), headaches, and even neck and shoulder pain.
4. Dental Health
Properly aligned teeth are easier to clean, reducing the risk of tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health issues. A normal bite allows for effective brushing and flossing, ensuring that all surfaces of your teeth are properly maintained.
Types of Bite Problems
Now, let’s delve into the different types of bite problems that can affect your dental health and overall well-being.
1. Overbite
An overbite, also known as a deep bite, occurs when your upper front teeth excessively overlap your lower front teeth. This can be caused by genetics, prolonged pacifier or bottle use, thumb sucking, or certain oral habits. While a slight overbite is common and usually not a cause for concern, an excessive overbite can lead to dental issues and aesthetic concerns.
Symptoms of an Overbite:
- Upper front teeth protruding over the lower teeth
- Difficulty biting into certain foods
- Speech difficulties, such as lisping
Treatment Options for Overbite:
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces or clear aligners can gradually shift the position of your teeth to correct the overbite.
- Extraction and dental appliances: In more severe cases, extraction of teeth may be necessary to create space for proper alignment. Dental appliances, such as headgear or palate expanders, may be used to assist in the correction of the overbite.
2. Underbite
An underbite is characterized by the lower jaw protruding beyond the upper jaw, causing the lower front teeth to overlap the upper front teeth. It can be caused by genetic factors, thumb sucking, prolonged pacifier use, or certain oral habits. An underbite can impact both the aesthetics and functionality of your bite.
Symptoms of an Underbite:
- Lower front teeth protruding beyond the upper front teeth
- Difficulty biting into certain foods
- Speech difficulties, such as difficulty pronouncing certain sounds
Treatment Options for Underbite:
- Early intervention: Orthodontic treatment at a young age can help guide the growth of the jaw and teeth, potentially minimizing the severity of the underbite.
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces or clear aligners can gradually shift the position of your teeth to correct the underbite. In more severe cases, orthognathic surgery may be required to reposition the jaw.
3. Excessive Spacing
Excessive spacing, also known as gaps or diastema, refers to gaps between teeth that are larger than normal. These spaces can occur due to various factors, such as missing teeth, undersized teeth, or an abnormal growth of the jawbone. While some individuals embrace their gaps as a unique feature, others may seek treatment for functional or aesthetic reasons.
Symptoms of Excessive Spacing:
- Visible gaps between teeth
- Difficulty biting into certain foods
- Increased risk of food impaction and gum problems
Treatment Options for Excessive Spacing:
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces or clear aligners can gradually close the gaps between teeth by shifting their positions.
- Dental restorations: In some cases, dental bonding, veneers, or crowns may be used to mask the gaps and create a more harmonious smile.
4. Deep Bite
A deep bite, also known as an overbite, occurs when the upper front teeth excessively overlap the lower front teeth. This can result in the lower incisors biting into the gum tissue behind the upper front teeth. A deep bite can lead to various dental issues, including tooth wear, gum problems, and discomfort.
Symptoms of a Deep Bite:
- Upper front teeth covering a significant portion of the lower front teeth
- Gum irritation and recession
- Wear on the biting surfaces of the front teeth
Treatment Options for Deep Bite:
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces or clear aligners can gradually correct the deep bite by repositioning the upper and lower teeth.
- Bite ramps or bite turbos: These small appliances can be placed on the back teeth to prevent the excessive overlapping of the front teeth.
5. Crossbite
A crossbite occurs when the upper teeth bite inside the lower teeth, either on one side or both sides of the mouth. This misalignment can affect both the front and back teeth and may be caused by genetic factors, jaw discrepancies, or certain oral habits.
Symptoms of a Crossbite:
- Upper teeth biting inside the lower teeth
- Asymmetrical jaw alignment
- Difficulty biting or chewing on one side of the mouth
Treatment Options for Crossbite:
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces or clear aligners can gradually correct a crossbite by shifting the positions of the teeth.
- Palatal expanders: In some cases, a palatal expander may be used to widen the upper jaw and correct the crossbite.
6. Crowding
Crowding occurs when there is insufficient space in the dental arch for all the teeth to align properly. It can result from a combination of genetic factors, small jaw size, or the presence of extra teeth. Crowding can lead to difficulties in oral hygiene, tooth decay, and aesthetic concerns.
Symptoms of Dental Crowding:
- Teeth overlapping or twisting to fit into limited space
- Difficulty flossing and brushing between crowded teeth
- Increased risk of tooth decay and gum disease
Treatment Options for Crowding:
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces or clear aligners can gradually align the crowded teeth by creating space and repositioning them.
- Tooth extraction: In some cases, extraction of one or more teeth may be necessary to create sufficient space for proper alignment.
7. Open Bite
An open bite is characterized by the upper and lower front teeth not touching when the back teeth are closed together. This can result in difficulty biting into certain foods and speech difficulties. Open bites can be caused by genetic factors, thumb sucking, tongue thrusting, or prolonged pacifier use.
Symptoms of an Open Bite:
- Upper and lower front teeth not touching when the back teeth are closed
- Difficulty biting into certain foods
- Lisping or other speech difficulties
Treatment Options for Open Bite:
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces or clear aligners can gradually close the open bite by repositioning the teeth.
- Oral habit correction: Addressing the underlying oral habits, such as thumb sucking or tongue thrusting, can aid in the correction of an open bite.
8. Normal Bite
A normal bite, also known as ideal occlusion, is characterized by the upper and lower teeth fitting together harmoniously. The upper teeth slightly overlap the lower teeth, allowing for effective chewing, clear speech, and optimal dental health.
Symptoms of a Normal Bite:
- Upper teeth slightly overlapping the lower teeth
- Comfortable chewing and biting
- Clear speech
Treatment Options for Maintaining a Normal Bite:
- Regular dental check-ups: Regular visits to your dentist or orthodontist can help monitor your bite and address any emerging dental issues.
- Good oral hygiene practices: Proper brushing, flossing, and regular cleanings can help maintain optimal dental health and prevent bite problems.
Conclusion
Having a normal bite is crucial for both dental health and overall well-being. Bite problems, such as overbites, underbites, excessive spacing, deep bites, crossbites, crowding, and open bites, can impact your ability to chew, speak clearly, and maintain good oral hygiene. Fortunately, various treatment options, including orthodontic interventions, dental appliances, and oral habit correction, can help correct these issues and restore a normal bite.
Remember to consult with your dentist or orthodontist to determine the best treatment plan for your specific bite problem. By addressing bite issues early on, you can enhance your dental health, improve your smile, and enjoy the benefits of a normal bite for years to come.
Important Links
https://orthodonticassoc.com/braces-invisalign/comprehensive-guide-to-common-bite-problems/
https://cardinalorthodontics.com/overbites-underbites-crossbites-bite-disorders/
https://www.serinoortho.com/patient-info/common-problems
https://www.gentledental.com/resources/articles/malocclusion
MedicAL DISCLAIMER
If you choose to use the information available on the Website without prior consultation with and consent of your physician, you are agreeing to accept full responsibility for your decisions and agreeing to hold harmless Randall K. McVey, DMD PA, its agents, employees, contractors, and any affiliated companies from any liability with respect to injury or illness to you or your property arising out of or connected with your use of this information.